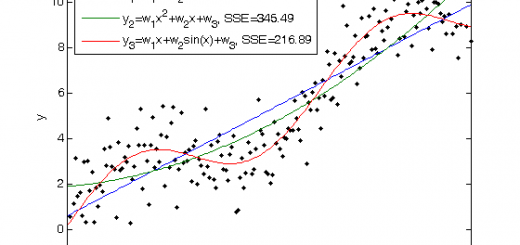
The problem of model generation is illustrated with a linear regression model of a single variable. See the example.
Contents
Make synthetic data using a model from generated set
To make such data we must assign a model and its parameters, set the independent variable and the calculate dependent variable.
f = inline('w(1)*x.^0 + w(2)*x.^(1/2) + w(3)*x.^1', 'w','x'); % model w = [1 -2 2]'; % parameters x = [0.1:0.1:1]'; % independent variable y = f(w,x); % dependent variable h = figure; hold on plot(x,y,'*');

Assign set of the primitive functions
Assume the intended model is a linear combination of the primitive functions
g{1} = 'x.^0';
g{2} = 'x.^(1/2)';
g{3} = 'x.^1';
g{4} = 'x.^(3/2)';
g{5} = 'x.^log(x)';
g
g =
'x.^0' 'x.^(1/2)' 'x.^1' 'x.^(3/2)' 'x.^log(x)'
Make the exhaustive search in the set of the models
Now we have 2^5-1 models.
% each element of the boolean vector defines is a primitive in the model of % not cnt = zeros(1,length(g)); % boolean vector ErrList = []; % keep errors of the model; CntList = []; % keep model descriptions for k = 1:2^length(g)-1 % for each model cnt = cntbin(cnt); % make a model description [X, f] = makelinmodel(g, cnt, x); % create a model w = pinv(X'*X)*X'*y; % tune parameters by Least Squares err = sumsqr(f(w,x)-y); % SSE, sum of square error % store the results ErrList = [ErrList err]; CntList = [CntList; cnt]; end
Select the best model according to its SSE
Consider a model of the best structure has minimal SSE
[dummy, idx] = min(ErrList); % find minimal SSE cnt = CntList(idx,:); % make the model description [X, f] = makelinmodel(g, cnt, x); % create the model w = pinv(X'*X)*X'*y; % tune parameters plot(x, f(w,x),'r-'); % plot results xlabel('\xi'); ylabel('y'); legend('data', 'model'); f
f =
Inline function:
f(w,x) = w(1)*x.^0+w(2)*x.^(1/2)+w(3)*x.^1

Appendix 1, makelinmodel.m
% function [X, f] = makelinmodel(g, cnt, x) % % make a linear model as an inline function and a matrix % % [X, f] = makelinmodel(cnt, g, x); % % % % g {string array 1,L} library of primitive functions % % cnt [1,L] binary counter 1 means the primitive in in the model % % x [m,1] data vector % % X [m,L] output matrix for the model, y = Xw % % f = f(w,x) a model function for linear regression % % % % Example % % g = {'x.^0', 'x.^1'}; % the primitive functions % % cnt = [1 1]; % include both function on the model % % x = rand(8, 1); % a column vector % % [X, f] = makelinmodel(g, cnt, x) % % y = f(ones(1,length(cnt)),x) % % X = []; % matrix y = Xw for the normal equation of the linear regression % str=''; % string to make a model (linear combination) % idx= 0; % number of item in the linear combination % for j = 1:length(cnt) % % if cnt(j) % X = [X eval(g{j})]; % add a column to matrix % idx = idx+1; % increase index of the weight % str = [str, 'w(', num2str(idx), ')*', g{j} ,'+']; % concatenate the model string % end % end % % if length(str)>1, % f = inline(str(1:end-1),'w','x'); % make the regression model % end % return
Appendix 2, cntbin.m
% function c = cntabover(c,a,b) % % % % c = cntbin(c) % % % % Vector of digits of a binary number plus one % % % % Example: % % c = zeros(1,4); % % for i=1:2^length(c)-1 % % c = cntbin(c) % % end % % % % returns % % c = % % 0 0 0 1 % % 0 0 1 0 % % ... % % 1 1 1 0 % % 1 1 1 1 % % % % i = length(c); % while i > 0 % if c(i)+1 <= 1 % c(i) = c(i)+1; % break % else % c(i) = 0; % i=i-1; % end % end % return